-

X1
Capacity and voltage range from low to high, widely distributed. Can be applied to lighting and consumer electronics.
X2
Capacity and voltage range from low to high, widely distributed. Can be applied to lighting and consumer electronics.
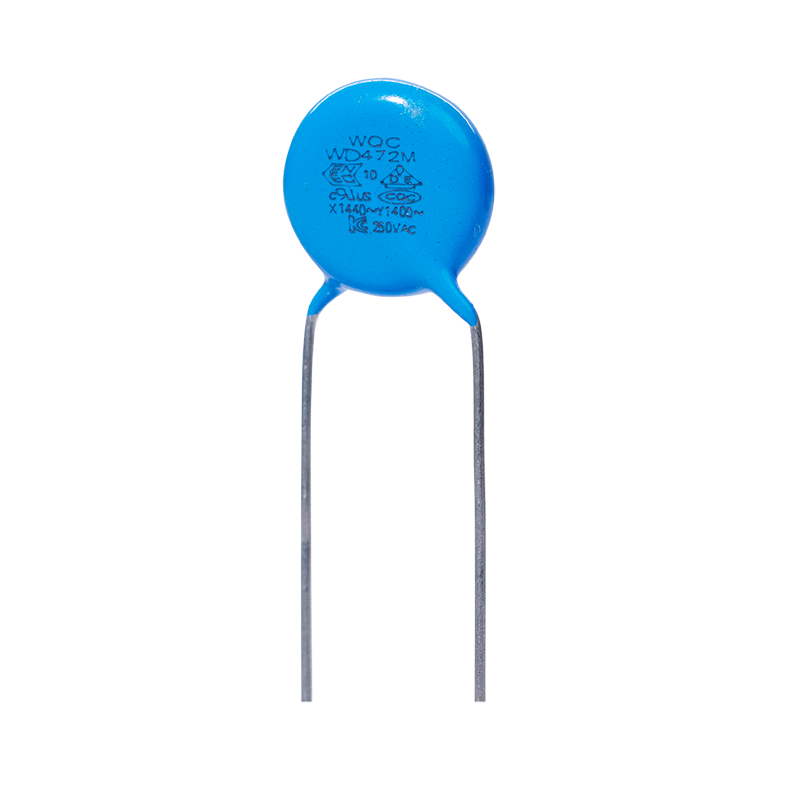

Y1
Capacity and voltage range from low to high, widely distributed. Can be applied to lighting and consumer electronics.
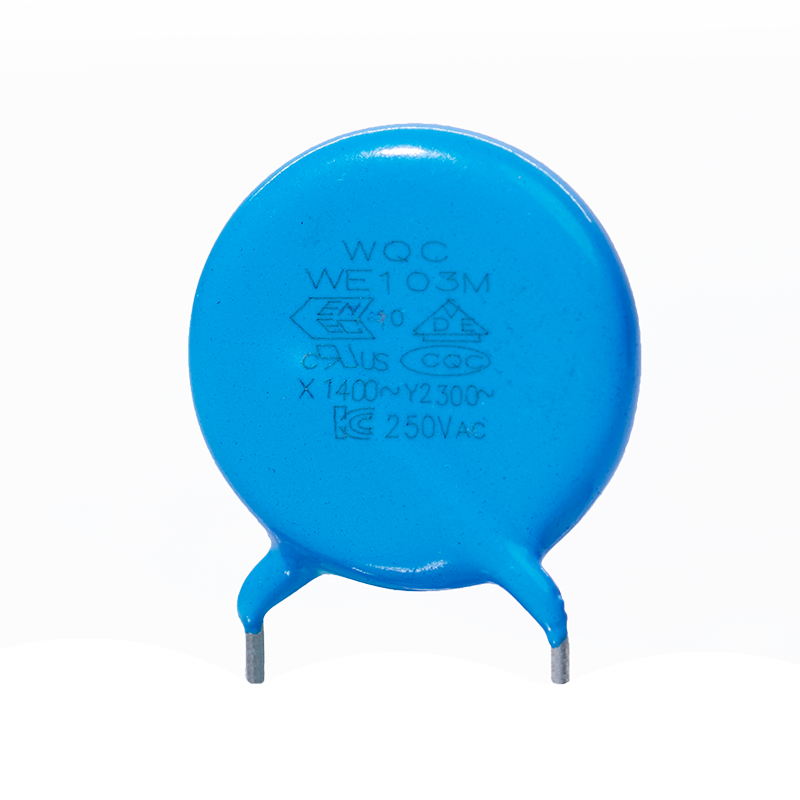

Y2
Capacity and voltage range from low to high, widely distributed. Can be applied to lighting and consumer electronics.
MEC Metal Film Box
Internal structure for increasing the rated voltage
2024-01-05
Self-healing of metallized film capacitors
2024-01-05
A Brief Analysis of Fault Handling Methods for Capacitors
2024-01-05
Method for Testing Fixed Capacitors
2024-01-05
Supercapacitors are also known as electric double-layer capacitors.
2024-01-05
Properties of Film Materials Used in Thin-Film Capacitors
2024-01-05
Service Hotline:
Contact
Phone: +86 13826981362
Tel:+86 076988956188
E-mail: wqc001@weiqingchina.com.cn
Address: Weiqing Electronics Co., Ltd., Floor 1, Building 12, No.7, Science and Technology 10th Road, Songshan Lake High-tech Development Zone, Songshan Lake Administrative Committee, Dongguan City, Guangdong Province
Mobile Website

Scan Consultation