-

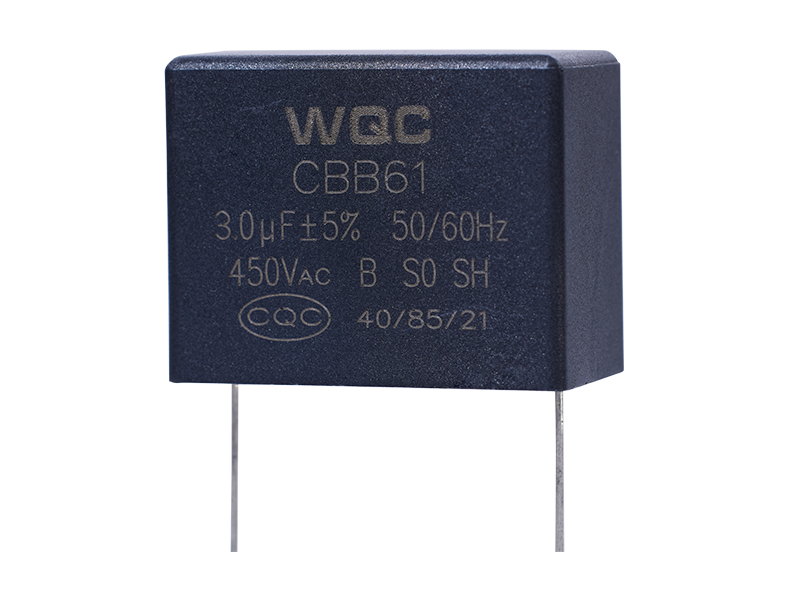
X1
Capacity and voltage range from low to high, widely distributed. Can be applied to lighting and consumer electronics.
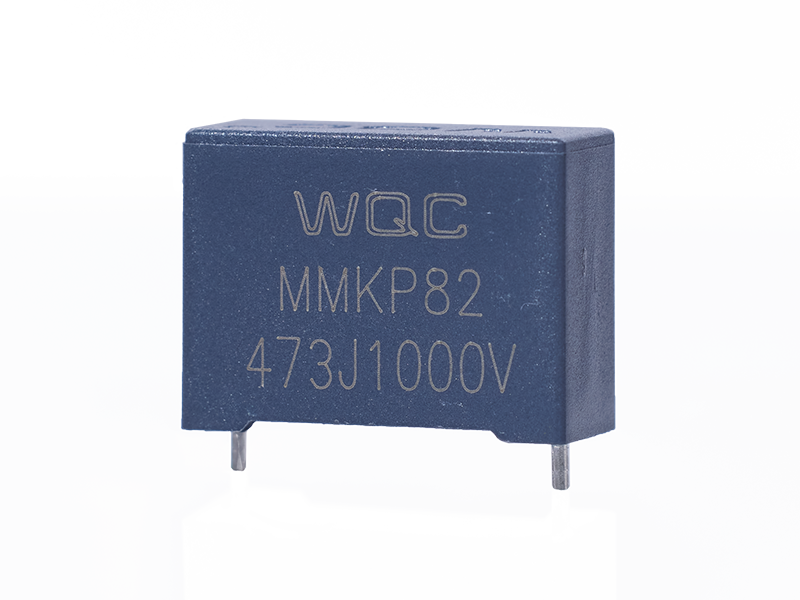
X2
Capacity and voltage range from low to high, widely distributed. Can be applied to lighting and consumer electronics.

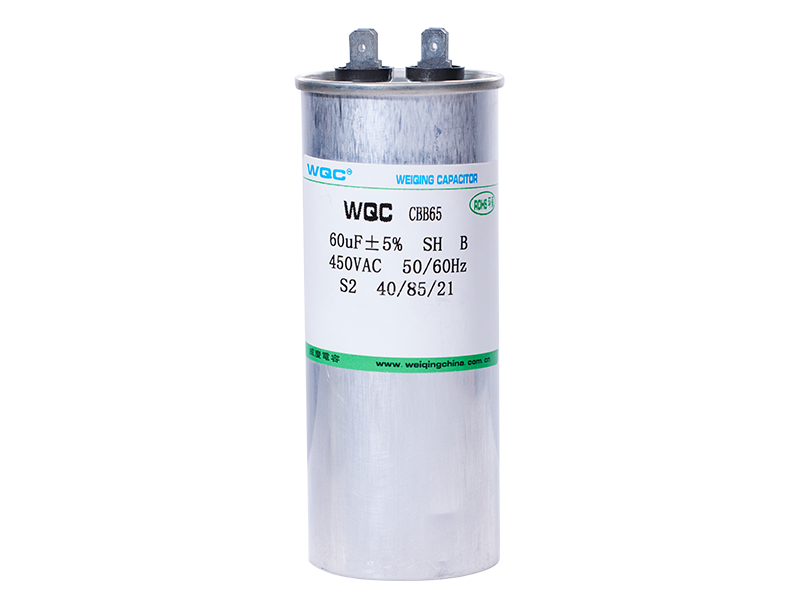
Y1
Capacity and voltage range from low to high, widely distributed. Can be applied to lighting and consumer electronics.

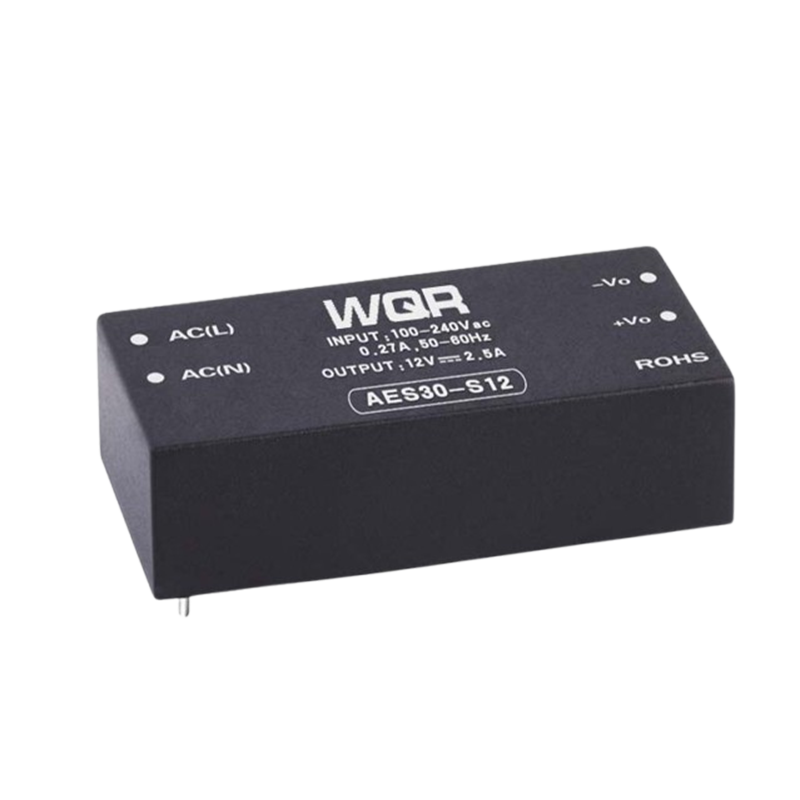
Y2
Capacity and voltage range from low to high, widely distributed. Can be applied to lighting and consumer electronics.
MEC Metal Film Box
Film Capacitor Introduction
Release time:
2024-01-05 17:24
Source:
Film capacitors, plastic film capacitors, film dielectric capacitors or polymer film capacitors, collectively referred to as film capacitors and power film capacitors, is a kind of insulating plastic film as the dielectric, sometimes with paper as the electrode carrier of the capacitor. According to the required dielectric strength, the dielectric film is drawn to an extremely thin thickness by a special process, and then equipped with electrodes. The electrodes of the film capacitor can be metallized aluminum or zinc, applied directly to the surface of the plastic film, or a separate metal foil. Two of these conductive layers are wound into cylindrical windings, typically flattened to reduce mounting space requirements on a printed circuit board, or laminated as a plurality of individual layers stacked together to form the capacitor body. Film capacitors, along with ceramic capacitors and electrolytic capacitors, are the most common type of capacitor in electronic devices and are used in many AC/DC microelectronics and electronic circuits. A related component type is a power (film) capacitor. Although the materials and construction techniques for high-power film capacitors are very similar to those used for ordinary film capacitors, for historical reasons, capacitors of high to very high power ratings for power systems and electrical devices are usually classified separately. As modern electronic devices gain the ability to handle power levels previously exclusive to power components, the distinction between electronics and power ratings becomes less pronounced. In the past, the boundary between these two series was about 200 volt-amperes of reactive power, but modern power electronics can handle ever-increasing power levels.
Previous Page
Next Page
Related News
Increase the internal structure of the rated voltage
The voltage ratings for different film materials depend on factors such as film thickness, material quality (free of physical defects and chemical impurities), ambient temperature and operating frequency, and the safety margin for breakdown voltage (dielectric strength). In general, however, the rated voltage of a film capacitor depends primarily on the thickness of the plastic film. For example, with the minimum usable film thickness of a polyester film capacitor (about 0.7 μm), a capacitor rated at 400V DC can be produced. If a higher voltage is required, a thicker plastic film is usually used
Self-healing of metallized film capacitors
Metallized film capacitors have self-healing properties that are not available in film/foil configurations. When a sufficient voltage is applied, point defect shorts between the metallized electrodes can evaporate due to the high arc temperature because the dielectric plastic material at the breakdown point and the metallized electrodes around the breakdown point are both very thin (about 0.02 to 0.05 microns). The point defect cause of the short circuit is burned, and the resulting steam pressure also blows the arc away. This process can be completed in less than 10 μs
Brief Analysis of Fault Treatment of Capacitor
When the fuse of the capacitor is blown, it shall be reported to the dispatcher, and the circuit breaker of the capacitor shall be opened after obtaining the approval. Cut off the power supply to discharge it, and conduct external inspection first, such as whether there are flashover marks on the outside of the casing, whether the shell is deformed, whether there is oil leakage and whether there is short circuit in the grounding device, etc., and measure the insulation resistance value between poles and poles to ground, and check whether the capacitor bank wiring is complete and firm, and whether there is phase loss
Detection method of fixed capacitor
1. Detect the small capacitance below 10pF: because the fixed capacitor capacity below 10pF is too small, using a multimeter to measure, can only qualitatively check whether there is leakage, internal short circuit or breakdown. When measuring, a multimeter R× 10k block can be selected, and two pens can be used to connect the two pins of the capacitor arbitrarily, and the resistance value should be infinite. If the measured resistance (pointer swing to the right) is zero, then the capacitor leakage damage or internal breakdown.
Supercapacitors are also known as electric double-layer capacitors.
Supercapacitor, also known as electric double layer capacitor and electrochemical capacitor, is a new type of electrochemical energy storage device with electrochemical performance between traditional capacitors and batteries. It mainly includes four parts: electrode, electrolyte, current collector and separator. It mainly stores energy through the electric double layer capacitance and the Faraday quasi-capacitance generated by the redox reaction. Generally speaking, the energy storage of supercapacitors is reversible, so it can be used to solve problems such as battery memory. At present, the application range of supercapacitors is very wide.
Service Hotline:
Contact
Phone: +86 13826981362
Tel:+86 076988956188
E-mail: wqc001@weiqingchina.com.cn
Address: Weiqing Electronics Co., Ltd., Floor 1, Building 12, No.7, Science and Technology 10th Road, Songshan Lake High-tech Development Zone, Songshan Lake Administrative Committee, Dongguan City, Guangdong Province
Mobile Website

Scan Consultation